Plan-9, Exploitable Smart Contracts, Meta released LLaMA, ControlNet - CS News #6
Welcome to CS News #6!
CS News helps you keep track of the latest news in different technology domains like AI, Security, Software development, Blockchain/P2P and discover new interesting projects and techniques!
💡 What was the Plan-9 project about?
Plan-9 is a distributed OS that was initially released in 1992 by Bell Labs engineers and Open Sourced in 2000 with the goal to be the successor of UNIX focused on modularity, security and scalability.
The project was initiated by Rob Pike (UTF-8, Go), Ken Thompson (co-creator of Unix, B, UTF-8, Go and grep) , Dave Presotto and Phil Winterbottom.
The project pushed the UNIX philosophy of “everything as a file” even further by introducing:
/proc: a virtual filesystem where running processes are represented as files. It can be used to fetch information like process IDS, memory usage or and file descriptors. This filesystem organization reflects the process tree hierarchy/net: an other new virtual filesystem to represent network resources like interfaces, sockets, protocols
The Plan-9 filesystem is distributed, which allows users to create & interact with files, processes and network ressources of remote machines as if they were local resources, in a way achieving the idea of a Global Computer. This has crazy utility: you can move files or processes from one machine to another without affecting their state for example.
The project also introduced the idea of private namespaces, to allow process to create isolated environments in order to run untrusted / malicious code for example.
Plan-9 engineers also focused their work on graphics and shipped it with Graphical Interfaces out of the box to make it more accessible for end users.
But with the rising popularity of UNIX (designed by Plan-9 creators), and because of a low focus on distribution, Plan-9 did not find a lot of success. The final official release was in 2015, since then it is only maintained by a niche community of contributors.
Even if this project never got super popular, a lot of its principles and innovations were re-used in similar projects, like modern UNIXes, for example:
UTF-8character encoding (developed by Plan-9 team)9P2000, Plan-9’s protocol for remote files accessrfork, Plan-9’s process creation mechanism/proc, implemented in FreeBSD and inspired Linux’s /proc filesystem,and many more: Plan-9’s window manager, Plan-9’s private namespaces influenced virtualisation technologies etc.
Learn more here.
🔍 Analysis of Exploitable Smart Contracts
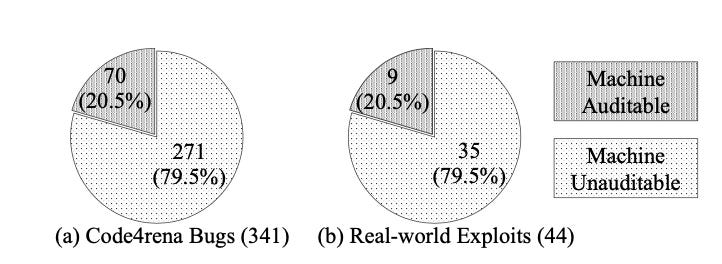
A team of security researcher analyzed more than 500 blockchain Smart Contracts bugs reported between 2021 and 2022 (on specialized bug bounty platforms like code4arena) to showcase the status of security tooling and common vulnerabilities in the blockchain ecosystem. Here is what we can learn from this report
The amount lost due to exploits is way higher than the amount of bug bounties paid, which shows the demand for more bug hunters and auditors in the space.
Most findings are not detected by the current security analysis tools (multiple static analyzers like Slither, fuzzers, symbolic execution and formal verification tools where tested here), which shows the importance of manual reviews from specialised auditors and the margin of progress for automatic vulnerability discovery tooling
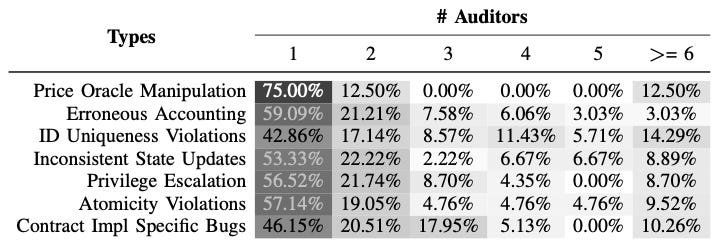
By taking into consideration the number of auditors per bug found, this paper shows which bugs are the hardest to find during audits, by order of difficulty:
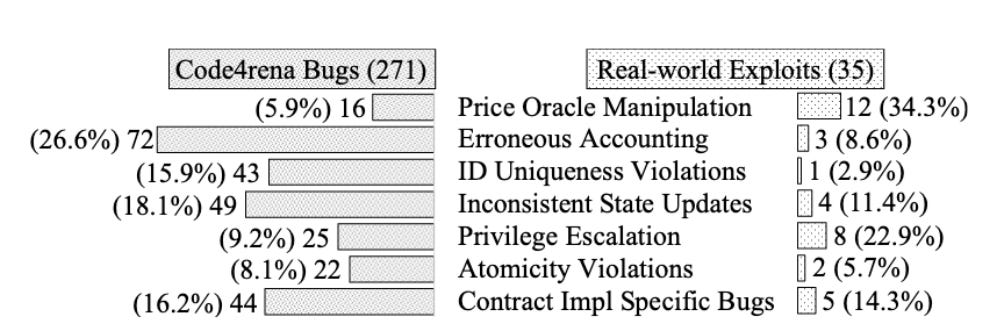
They have also showed that real-world most exploited bugs are actually difficult to find (like Price Oracle Manipulation):
Read more here.
🦙 Meta introduces LLaMA : a 65b parameter LLM
Meta introduced a new Large Language Model (LLM) named LLaMA, trained on 20 different languages and aiming to enable “research community who doesn’t have access to large amounts of infrastructure to study these models”. Indeed, it has been harder with time for research community to keep up with over-parametrized model always requiring more compute ressources. This new model leads to the creation of ChatLLaMA by Nebuly AI, a model made to mimic the capabilities of ChatGPT.
However LLaMA was initially not accessible other than through a form that you must fill to be approved my meta, leading to some criticism. Few days later a post on 4chan leaked a torrent to download LLaMA 7b-64b. This leak, as well as leading to people making people fun of Meta, enables people to run their own LLaMA and test the model performances that turn out to be disappointing.
🎛 ControlNet
A paper named Adding Conditional Control to Text-to-Image Diffusion Models revealed the ControlNet neural network structure that can learn task-specific conditions. Authors “report that large diffusion models like Stable Diffusion can be augmented with ControlNets to enable conditional inputs like edge maps, segmentation maps, keypoints, etc”.
Generally to adapt a neural network to a task-specific condition (i.e generating an image from a heat map) can be done either by transfer learning or by fine-tuning the model. Here ControlNet presents itself as a third option “as fast as fine-tuning” and “robust even when the training dataset is small (< 50k)”.
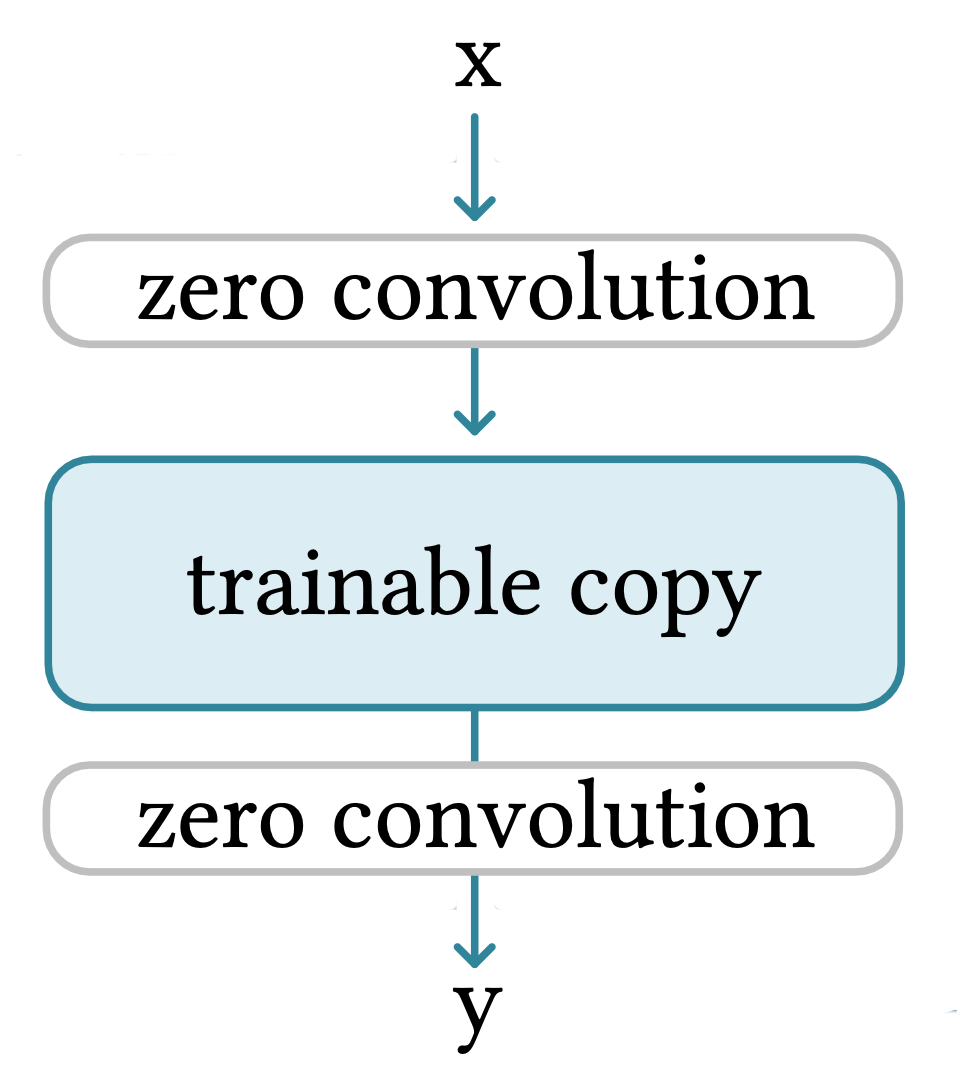
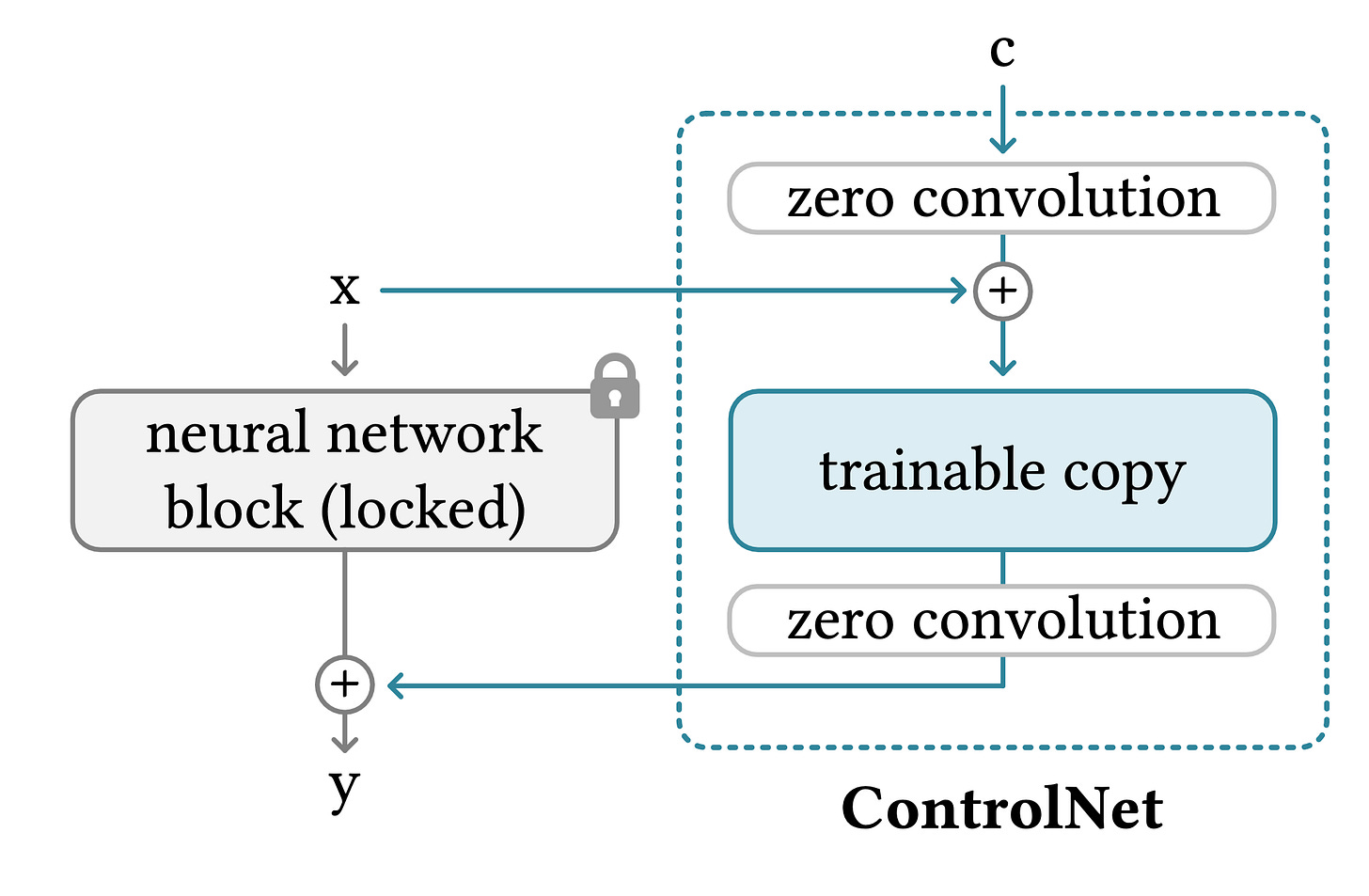
In this structure the ControlNet clones the weights of the model into a “trainable copy” and keeps the original model as the “locked copy”. The trainable copy sees its block linked by a “zero convolution” layer before and after each aimed blocks. A zero convolution layer being a convolution layer (i.e 1x1 kernels) initialized at 0 and growing from 0 to an optimized value.
The trainable copy is trained on a task-specific dataset to learn the conditional control, thus optimizing both the parameters of the trainable model’s block and the zero-convolution layers.
Afterwards at inference time the trainable copy receives as input an external condition vector $c$ representing the condition we want to impose to our model and is linked to the locked copy’s block such as :
with
Θbeing the locked model’s parameters,Θthe trainable model’s parameters,Θz1the first zero-convolution’s parameters,Θz2the first zero-convolution’s parameters,xthe model’s input,Zthe zero-convolution layer,Fthe model’s block andycbeing the model’s output following the condition constraint.
As the authors stated “the motivation of making such copies rather than directly training the original weights is to avoid overfitting when dataset is small […]” as the original model’s parameters remain unchanged within the locked copy.
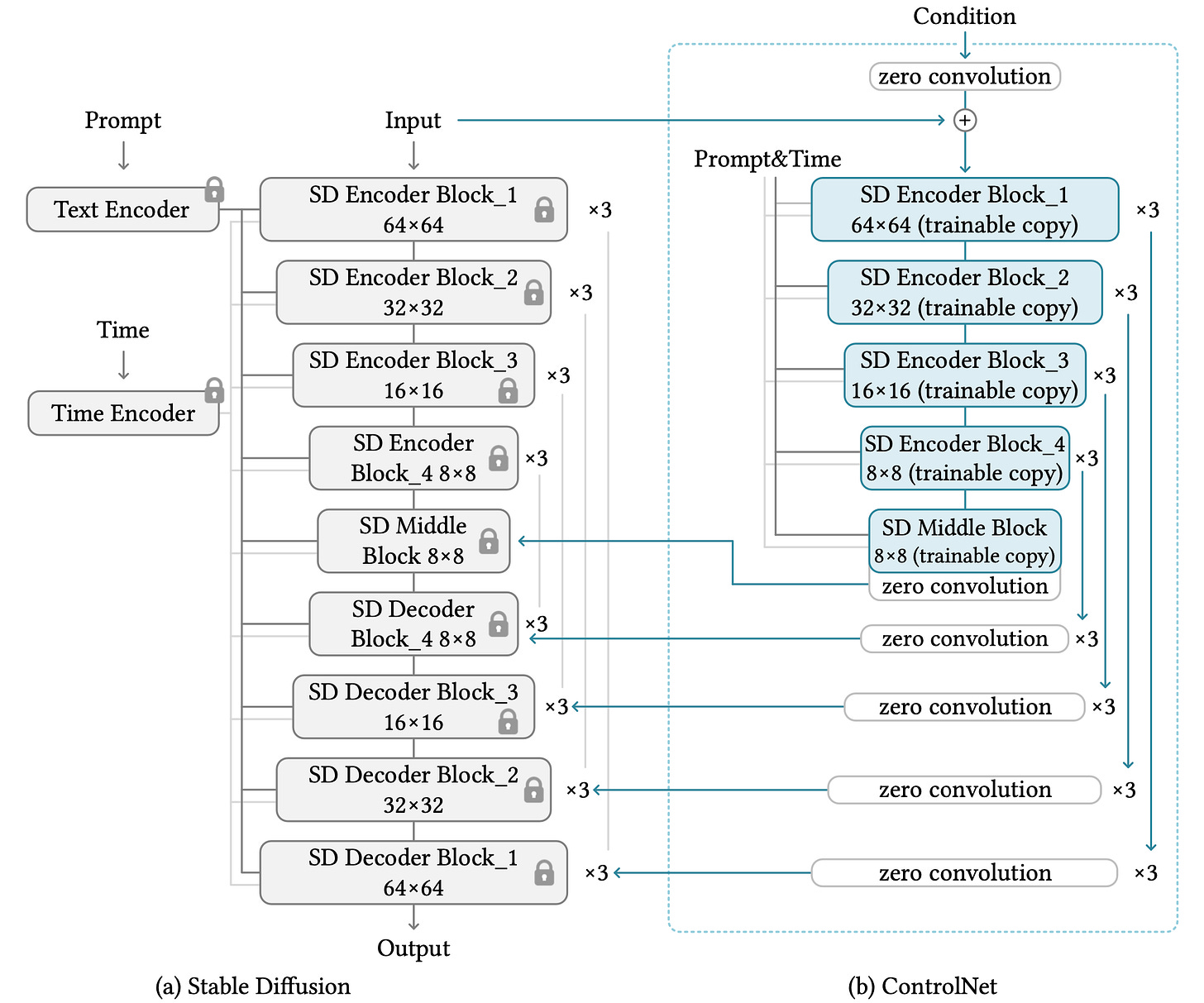
This process is adapted to the Stable Diffusion model as shown below:
Read the paper here.