On-Chain AI models, Git vulnerabilities, the future of Programming - CS News #3
Welcome to CS News #3!
The CS newsletter helps you keep track of the latest news in different technology domains like AI, Security, Software development, Blockchain/P2P and discover new interesting projects and techniques!
💡Project Highlight: Giza, on-chain Artificial Intelligence models
Some Context to start with:
Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) is emitted by a Prover to prove to third parties (Verifiers) that a statement is true without sharing too much information. In case of computation, it means proving the result of a computation without sharing the algorithm or inputs used for example.
Starknet is a p2p network maintaining a verifiable state (blockchain). When this state is computed by a node (by executing user transactions), it emits Zero Knowledge Proofs which are stored on the underlying Ethereum chain (which is validated by more than 500 000 nodes worldwide). This way any state change of Starknet can be easily verified by anyone without needing to recompute (ie execute transactions) all the state from the start of the network nor knowing every internal logics of applications deployed and executed on the network.
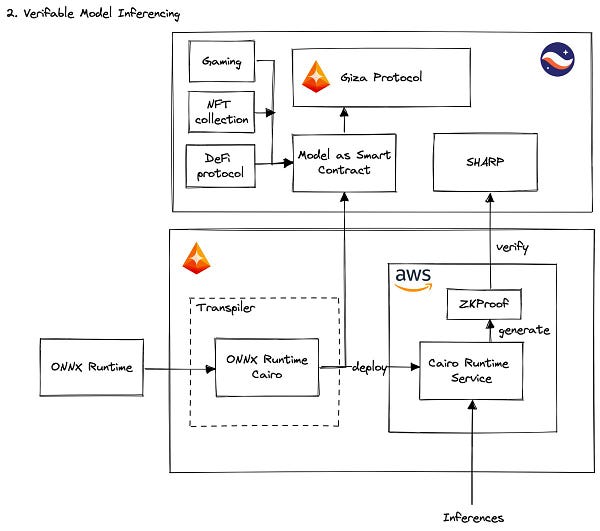
Giza is a project developed in the Starknet ecosystem to deploy Machine Learning models and execute them. You can deploy your ONNX models as Smart Contracts (ie on-chain applications that can be interacted with via transactions and that may impact the blockchain state), and enjoy the benefit of the Starknet blockchain and Ethereum ecosystem:
low/0% downtime
decentralization
fault tolerance
deployment in a single transaction with super low cost
Giza also works on verifiable training of models, this way you can verify a Machine Learning model trained on a certain dataset without having access to all the data points of it, or ensure a model is not biased without sharing the actual model.

🔒 GitHub announced Git security vulnerabilities
Last Tuesday, GitHub announced 3 CVEs that can trigger Remote Code Execution:
CVE-2022-41903 and CVE-2022-23521 which both lead to arbitrary heap reads and writes using integer overflows. The first one exploits the
git log --formatrendering when processing certain padding operators, the second one the.gitattributesfile parser which has multiple integer overflows when attributes have too long names or too many attributes. These arbitrary reads and writes on the stack make it possible for an attacker to perform Remote Code Execution on any computer running the vulnerable git version.CVE-2022-41953 impacts git GUI for windows, which can run untrusted code when performing its spell checking.
The audit was sponsored by the Open Source Technology Improvement Fund and fixed by Gitlab, GitHub and Git Security teams.
🔭 Google AI goals and roadmap
Google restates its interest in AI and gives us insights on its roadmap by kicking off a series in which researchers across Google will highlight some progress made in 2022 and present its vision for 2023.
In this kick-off Google retraces four main aspects in which 2022 has been focused on :
Language Models with PaLM, and other works on LLMs
Generative Models with Imagen, PixelRNN or DreamBooth
And concludes that 2023 and beyond will surely be marked by advances in the quality and speed of LLMs, media generation, or even on-device multi-modal models.
👉 You can also find a more global of Google’s view on AI, its focus and why it matters here.
⏱ The future of programming
We are used to common APIs with pre-determined endpoints expecting specific inputs, but what if we could create an API that could answer all our requests, whatever our queries and intents are? This would result in an almost unlimited possibilities API. That’s the concept highlighted by @DinuMariusC in his project SymbolicAI. The question is how to translate AI research on LLMs into proper, usable day-to-day products?
More informations of SymbolicAI
Interesting stuff
Google DeepMind says it’ll launch a more grown-up ChatGPT soon
Best practices to use foundry, for Ethereum Smart Contract developers
How Nvidia’s CUDA Monopoly In Machine Learning Is Breaking - OpenAI Triton And PyTorch 2.0
Running a 130b parameters model on a local machine using int4
Reprogramming frozen Conformer-ASR for more languages recognition
A brain-computer interface that turns speech-related neural activity into text
Google Calls In Help From Larry Page and Sergey Brin for A.I. Fight
Human-Timescale Adaptation in an Open-Ended Task Space - by DeepMind
Let’s discuss!
Follow on twitter @CobolStone
Join the community discord




